

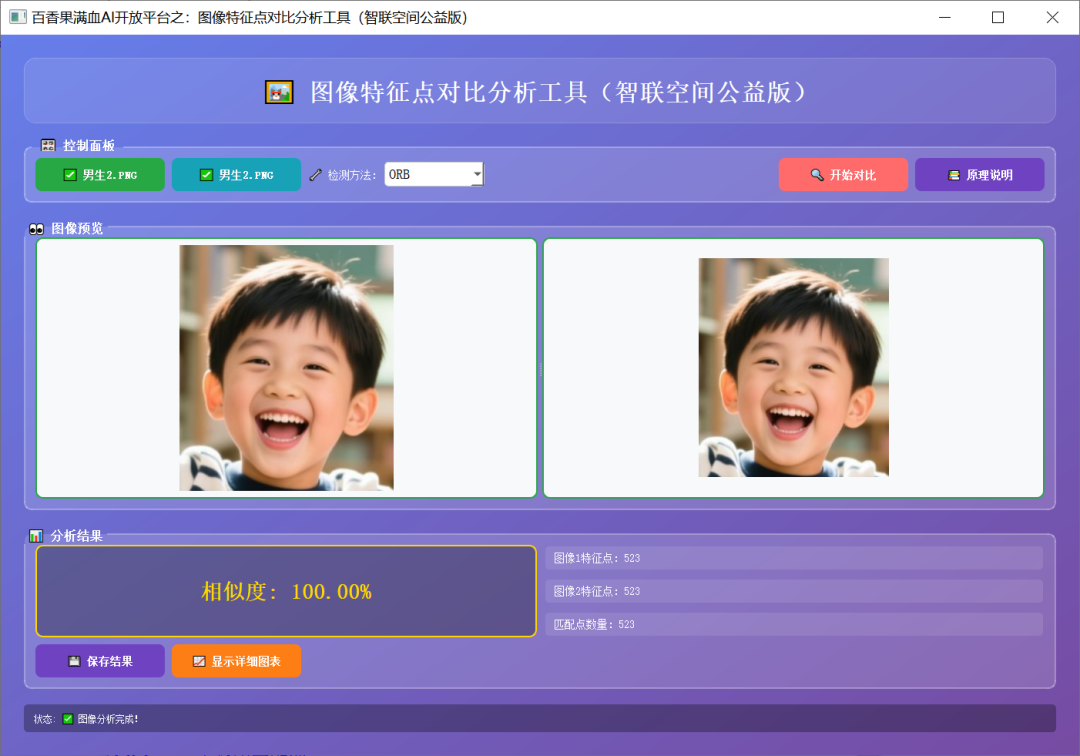
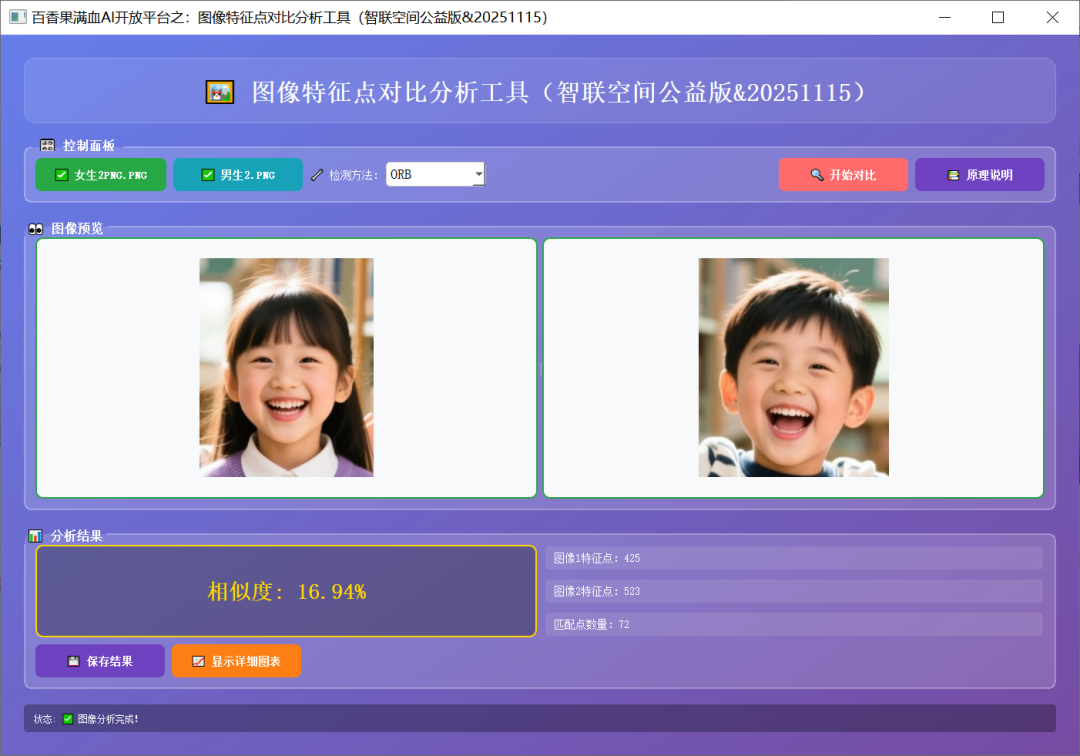
百香果满血AI开放平台之:图像特征点对比分析工具)
AI创作:王爱胜 @ 智联空间






def try_read_image(file_path): “””尝试用多种方法读取图像””” # 方法1: 使用imageio try: import imageio.v3 as iio img = iio.imread(file_path) if img is not None and img.size > 0: return True, “验证通过 (imageio)” except Exception as e: pass
# 方法2: 使用skimage try: from skimage import io img = io.imread(file_path) if img is not None and img.size > 0: return True, “验证通过 (skimage)” except Exception as e: pass
# 方法3: 使用PIL try: from PIL import Image with Image.open(file_path) as img: img.verify() return True, “验证通过 (PIL)” except Exception as e: pass
# 方法4: 使用OpenCV作为最后手段 try: img = cv2.imread(file_path) if img is not None and img.size > 0: return True, “验证通过 (OpenCV)” except Exception as e: pass
return False, “无法读取图像文件(可能已损坏或不支持的格式)”
class UniversalImageReader: “””通用图像读取器,使用多种库确保兼容性”””
@staticmethod def read_image(file_path): “””读取图像,自动选择最佳方法””” methods = [ UniversalImageReader._read_with_imageio, UniversalImageReader._read_with_skimage, UniversalImageReader._read_with_pil, UniversalImageReader._read_with_opencv ]
for method in methods: try: img = method(file_path) if img is not None: #print(f”成功使用 {method.__name__} 读取图像”) return img except Exception as e: #print(f”{method.__name__} 读取失败: {e}”) continue
raise ValueError(f”所有方法都无法读取图像文件: {file_path}”)
@staticmethod def _read_with_imageio(file_path): “””使用imageio读取图像””” try: import imageio.v3 as iio img = iio.imread(file_path) if img is not None and img.size > 0: # imageio返回RGB,需要转换为BGR供OpenCV使用 if len(img.shape) == 3 and img.shape[2] == 3: img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) elif len(img.shape) == 3 and img.shape[2] == 4: img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGBA2BGR) return img except Exception as e: raise e return None
@staticmethod def _read_with_skimage(file_path): “””使用skimage读取图像””” try: from skimage import io, color img = io.imread(file_path) if img is not None and img.size > 0: # skimage可能返回各种格式,统一转换为BGR if len(img.shape) == 3: if img.shape[2] == 3: # RGB img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) elif img.shape[2] == 4: # RGBA img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGBA2BGR) elif len(img.shape) == 2: # 灰度图 img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) return img except Exception as e: raise e return None
@staticmethod def _read_with_pil(file_path): “””使用PIL读取图像””” try: from PIL import Image with Image.open(file_path) as pil_img: # 转换为RGB模式 if pil_img.mode != ‘RGB’: pil_img = pil_img.convert(‘RGB’)
# 转换为numpy数组 img_array = np.array(pil_img) # PIL图像是RGB,OpenCV需要BGR img_array = cv2.cvtColor(img_array, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR) return img_array except Exception as e: raise e return None
@staticmethod def _read_with_opencv(file_path): “””使用OpenCV读取图像(最后尝试)””” try: # 尝试不同的读取模式 for mode in [cv2.IMREAD_COLOR, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED, cv2.IMREAD_ANYCOLOR]: img = cv2.imread(file_path, mode) if img is not None and img.size > 0: # 如果是灰度图,转换为BGR if len(img.shape) == 2: img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) return img except Exception as e: raise e return None
class ComparisonThread(QThread): “””用于在后台执行图像比较的线程””” finished = pyqtSignal(dict) progress = pyqtSignal(str) error = pyqtSignal(str)
def __init__(self, image1_path, image2_path, method=’ORB’): super().__init__() self.image1_path = image1_path self.image2_path = image2_path self.method = method
def run(self): try: # 首先验证图像文件 self.progress.emit(“正在验证图像文件…”)
valid1, msg1 = ImageValidator.validate_image_file(self.image1_path) if not valid1: self.error.emit(f”图像1验证失败: {msg1}”) return
valid2, msg2 = ImageValidator.validate_image_file(self.image2_path) if not valid2: self.error.emit(f”图像2验证失败: {msg2}”) return
# 创建改进的比较器 self.progress.emit(“正在初始化特征检测器…”) comparator = RobustImageFeatureComparator(method=self.method)
self.progress.emit(“正在读取和预处理图像…”) self.progress.emit(“正在检测图像特征点…”)
result = comparator.compare_images(self.image1_path, self.image2_path)
self.progress.emit(“正在生成可视化结果…”) self.finished.emit(result)
except Exception as e: self.error.emit(f”处理过程中发生错误: {str(e)}”)
class RobustImageFeatureComparator: “””鲁棒的图像特征比较器”””
def __init__(self, method=’ORB’, min_match_count=10): self.method = method self.min_match_count = min_match_count self.feature_detector = self._create_detector()
def _create_detector(self): “””创建特征检测器””” if self.method == ‘ORB’: return cv2.ORB_create(nfeatures=2000) elif self.method == ‘SIFT’: try: # 尝试使用SIFT return cv2.SIFT_create(nfeatures=2000) except: #print(“SIFT不可用,使用ORB代替”) return cv2.ORB_create(nfeatures=2000) elif self.method == ‘AKAZE’: return cv2.AKAZE_create() elif self.method == ‘BRISK’: return cv2.BRISK_create() else: return cv2.ORB_create(nfeatures=2000)
def preprocess_image(self, img): “””图像预处理””” # 检查图像尺寸,如果太大则调整大小 height, width = img.shape[:2] max_dimension = 1600 if height > max_dimension or width > max_dimension: scale = max_dimension / max(height, width) new_width = int(width * scale) new_height = int(height * scale) img = cv2.resize(img, (new_width, new_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) #print(f”图像尺寸调整: {width}x{height} -> {new_width}x{new_height}”)
return img
def detect_and_compute(self, image_path): “””检测图像特征点和描述符””” try: # 使用通用图像读取器 #print(f”正在读取图像: {image_path}”) img = UniversalImageReader.read_image(image_path)
if img is None: raise ValueError(f”无法读取图像: {image_path}”)
# 图像预处理 img = self.preprocess_image(img)
# 转换为灰度图 if len(img.shape) == 3: gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) else: gray = img.copy()
# 图像增强以提高特征检测效果 enhanced_gray = self.enhance_image(gray)
# 检测特征点和计算描述符 #print(“正在检测特征点…”) keypoints, descriptors = self.feature_detector.detectAndCompute(enhanced_gray, None)
# 如果特征点太少,尝试在原图上检测 if keypoints is None or len(keypoints) < 20: #print(“特征点过少,尝试在原图上检测…”) keypoints, descriptors = self.feature_detector.detectAndCompute(gray, None)
#print(f”检测到 {len(keypoints) if keypoints else 0} 个特征点”) return img, keypoints, descriptors
except Exception as e: raise ValueError(f”处理图像时出错 {image_path}: {str(e)}”)
def enhance_image(self, gray): “””图像增强以提高特征检测效果””” # 直方图均衡化 enhanced = cv2.equalizeHist(gray)
# 高斯模糊去噪 enhanced = cv2.GaussianBlur(enhanced, (3, 3), 0)
# 对比度增强 alpha = 1.5 # 对比度控制 beta = 0 # 亮度控制 enhanced = cv2.convertScaleAbs(enhanced, alpha=alpha, beta=beta)
return enhanced
def match_features(self, descriptors1, descriptors2): “””匹配特征点””” if descriptors1 is None or descriptors2 is None: return []
if len(descriptors1) == 0 or len(descriptors2) == 0: return []
# 创建BFMatcher if self.method == ‘ORB’: matcher = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True) else: matcher = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2, crossCheck=True)
try: matches = matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2) # 按距离排序 matches = sorted(matches, key=lambda x: x.distance) return matches except Exception as e: #print(f”特征匹配失败: {e}”) return []
def calculate_similarity(self, matches, keypoints1, keypoints2): “””计算相似度得分””” if len(matches) < self.min_match_count: return 0.0, []
try: # 使用RANSAC过滤错误匹配 src_pts = np.float32([keypoints1[m.queryIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2) dst_pts = np.float32([keypoints2[m.trainIdx].pt for m in matches]).reshape(-1, 1, 2)
# 计算单应性矩阵 M, mask = cv2.findHomography(src_pts, dst_pts, cv2.RANSAC, 5.0)
if mask is None: return 0.0, []
# 获取内点(正确匹配) inlier_matches = [matches[i] for i in range(len(matches)) if mask[i] == 1]
# 计算相似度 total_keypoints = min(len(keypoints1), len(keypoints2)) if total_keypoints > 0: similarity = len(inlier_matches) / total_keypoints * 100 similarity = min(similarity, 100.0) # 限制最大值为100% else: similarity = 0.0
return similarity, inlier_matches except Exception as e: #print(f”相似度计算失败: {e}”) return 0.0, []
def compare_images(self, image1_path, image2_path): “””比较两张图像””” # 检测特征 img1, kp1, desc1 = self.detect_and_compute(image1_path) img2, kp2, desc2 = self.detect_and_compute(image2_path)
kp1_count = len(kp1) if kp1 else 0 kp2_count = len(kp2) if kp2 else 0
#print(f”图像1检测到 {kp1_count} 个特征点”) #print(f”图像2检测到 {kp2_count} 个特征点”)
# 匹配特征 matches = self.match_features(desc1, desc2) #print(f”找到 {len(matches)} 个初始匹配点”)
# 计算相似度 similarity, good_matches = self.calculate_similarity(matches, kp1, kp2) #print(f”过滤后得到 {len(good_matches)} 个正确匹配点”) #print(f”相似度: {similarity:.2f}%”)
return { ‘image1’: img1, ‘image2’: img2, ‘keypoints1’: kp1, ‘keypoints2’: kp2, ‘matches’: good_matches, ‘similarity’: similarity }

更多AI纯血课与平台点击此处下载